Email has become an ever-present form of communication in the modern digital age and is used for a wide range of purposes, including personal communication, business communication, marketing, and more. Email has many advantages over other forms of communication, such as its speed, convenience, low cost, and the ability to send messages to multiple recipients simultaneously.
As email became the most common form of communication, especially in businesses, it also became a common form to spread fraud. In fact, according to the 2022 FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), the IC3 received 21,832 BEC complaints with adjusted losses of over $2.7 billion.
Email fraud, also known as email scams or phishing attacks, is a type of online fraud that involves the use of fraudulent emails to deceive recipients into giving away sensitive information or performing an action that benefits the fraudster. Email fraud typically involves the use of fake email messages that are designed to look like they are coming from a legitimate source, such as a bank, online retailer, or other trusted institution.
Luckily, there is a way where email domain owners can prevent these fraudulent email problems that might affect the business and its clients, by using a Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) policy.
What is a DMARC?
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that uses Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to verify the authenticity of an email sender's identity and provide instructions for how to handle emails that fail authentication.
It also allows email domain owners to specify which email servers are authorized to send emails on their behalf and provides a mechanism for receiving feedback about the email streams using DMARC reports. DMARC enables the email receivers to determine if an email message is legitimate or fraudulent by checking the SPF and DKIM results and applying policy according to the DMARC policy in the domain's DNS record.
DMARC provides a feedback mechanism that enables email receivers to report back to domain owners about the authentication status of messages sent from their domains. This feedback loop can help domain owners to identify and take action against any fraudulent use of their domain names in email messages.
In addition to the security benefits that a DMARC can provide, there are several more reasons why businesses should opt to use this authentication protocol.
Benefits of Using DMARC
To make an informed decision about whether to implement DMARC in your company, it's crucial to have a good understanding of the benefits it offers. Here are some of the reasons why businesses should consider using a DMARC:
Protection Against Email Fraud and Phishing Attacks
DMARC provides a mechanism for email authentication and reporting, which helps to prevent unauthorized use of a domain name in email messages. This can help to protect individuals and organizations from email fraud and phishing attacks. In a 2022 report by AAG, on cybercrime rates, of 1400 organizations surveyed, 80% believed it was likely they would suffer from an email-based cyber attack.
With a lot of reports being recorded on phishing attacks, Business Email Compromise (BEC), and other forms of email fraud, this must be a top priority of businesses especially when they are heavily dependent on email for their business.
Improved Email Deliverability
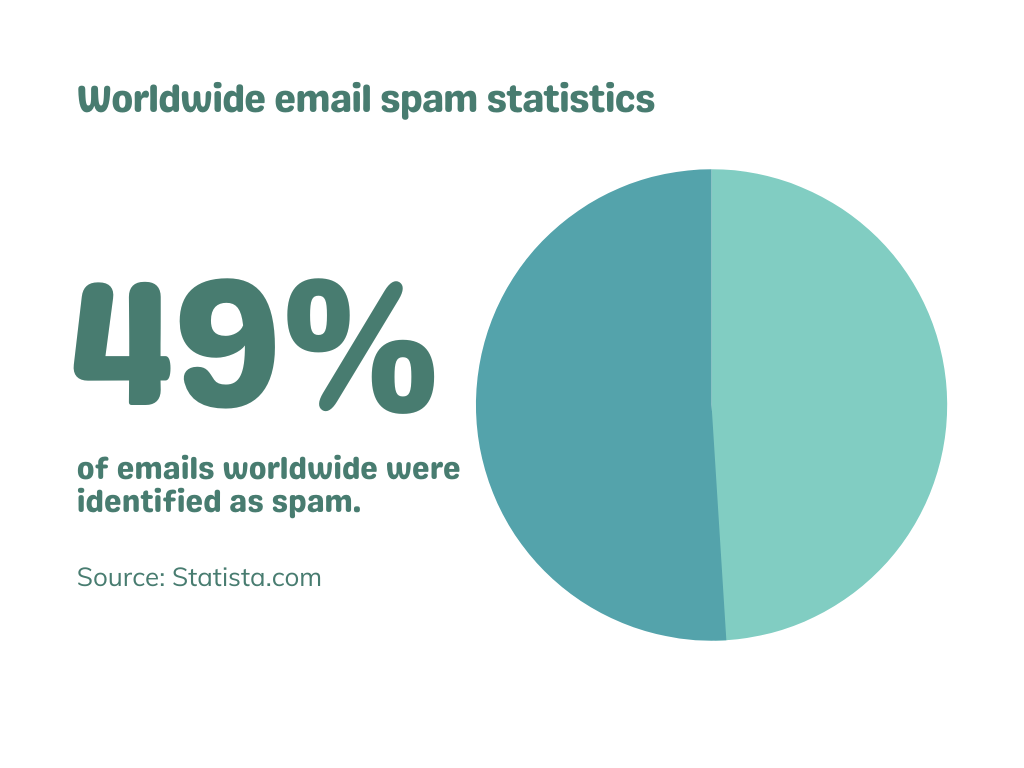
According to a report from Statista, in 2022, nearly 49 percent of all e-mails worldwide were identified as spam, up from 46 percent in 2021. Businesses should be aware of the statistics on email spam because it can have a significant impact on their email communication and overall business operations.
DMARC helps to ensure that legitimate emails are delivered to recipients' inboxes by verifying the authenticity of the sender's identity and reducing the risk of emails being marked as spam or rejected by email servers. This is vital for businesses that focus on targeting customers through email marketing.
Increased Visibility into Email Activity
DMARC provides detailed reports on email authentication results, which can help domain owners to identify and take action against any fraudulent use of their domain names in email messages.
The reports include information such as the number of emails sent using the domain name, the percentage of those emails that passed DMARC authentication, and details about any failed authentication attempts. The reports also include information about the IP addresses and domains used to send the emails, as well as information about the email authentication protocols used.
Enhanced Brand Reputation
By using DMARC, domain owners can protect their brand reputation by preventing unauthorized use of their domain names in email messages. This can help to build trust with customers and partners and protect against damage to the brand's reputation.
When a company implements DMARC, it can configure email servers to reject any email messages that fail DMARC authentication. This ensures that any unauthorized use of the company's domain name is prevented, protecting the company's reputation and maintaining customer trust.
Compliance with Email Security Standards
DMARC is a widely recognized email security standard that is supported by major email providers and is required for compliance with certain regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
It also encourages the adoption of email security standards by providing a framework for email authentication and reporting that can be used by all email providers. As more companies adopt DMARC, it becomes easier for email providers to identify and block fraudulent emails, making the internet a safer place for everyone.
DMARC Failure Common Reasons
DMARC has presented a lot of benefits that it could offer to help businesses and it has been an option for them to use, more importantly, because email has been one of the most common forms of communication of business to customers.
But for businesses that already implement DMARC for their email protocol, there are times that it can also experience failure. Here are some of the common reasons why DMARC fails:
Incorrect DNS Records
DMARC relies on specific DNS (Domain Name System) records to authenticate email messages. If these records are incorrect or not properly configured, DMARC may fail to authenticate email messages. This can result in the email message being marked as suspicious or rejected outright, depending on the DMARC policy that has been set.
SPF/DKIM Alignment Issues
DMARC requires that the SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records are properly aligned with the "From" header of the email message. If there is a mismatch between these records and the "From" header, DMARC may fail to authenticate the email message.
If DMARC fails to authenticate an email message due to alignment issues, the email may be marked as suspicious or rejected outright, depending on the DMARC policy that has been set. This can result in the email not being delivered or being delivered to the recipient's spam folder.
Incomplete Implementation
DMARC requires a complete implementation of both SPF and DKIM in order to properly authenticate email messages. If either of these protocols is not fully implemented, DMARC may fail to authenticate email messages.
Incomplete implementation of DMARC can occur when not all email domains associated with an organization are properly configured with DMARC policies. This means that some email messages may not be properly authenticated or protected by DMARC, leaving them vulnerable to phishing and other types of email fraud.
Email Service Provider Issues
If a DMARC Email Service Provider (ESP) has issues, it may be because ESPs do not properly handle DMARC policies and it can result in email messages being marked as suspicious or rejected outright, depending on the DMARC policy that has been set. This can result in the email not being delivered or being delivered to the recipient's spam folder.
How To Fix Email DMARC Failure
Fixing DMARC failures can involve several steps, depending on the root cause of the failure. Here are some common steps you can take to fix DMARC failures:
Review EMAIL DMARC Reports
First, review the DMARC reports to identify the cause of the failure. DMARC reports can provide valuable information about email activity, such as which emails passed or failed DMARC checks and which domains are sending emails on your behalf. This information can help you identify any misconfigurations or issues that are causing DMARC failures.
Check DNS Records
Check your DNS records, including SPF and DKIM records, to ensure that they are correctly configured. DMARC relies on the alignment of these records to authenticate email messages, so any misconfigurations can cause DMARC failures.
To avoid issues with DMARC authentication and email delivery, it's important to ensure that DNS records are properly configured and up-to-date. This may involve working with your email service provider or IT team to review and update your DNS settings. By properly configuring your DNS records, you can ensure that your DMARC policies are correctly implemented and that your email messages are properly authenticated and delivered.
Ensure Alignment
Make sure that the "From" header in your email messages aligns with the domain listed in your SPF and DKIM records. This alignment is critical to DMARC authentication, so any discrepancies can cause DMARC failures.
To avoid issues with alignment, it's important to ensure that the SPF and DKIM records are properly configured to match the "From" header in the email message. This may involve reviewing and updating the DNS records or working with your email service provider or IT team to ensure that the proper configurations are in place. By properly aligning SPF and DKIM records, you can ensure that your DMARC policies are correctly implemented and that your email messages are properly authenticated and delivered.
Adjust DMARC Policy
If you have a strict DMARC policy in place, consider adjusting it to a more permissive policy, such as "p=none". This will allow you to receive DMARC reports without rejecting email messages that fail DMARC authentication.
Contact Email Service Provider
If you are using an email service provider (ESP), contact them for assistance with resolving DMARC failures. They may be able to provide guidance on how to configure your DNS records or adjust your DMARC policy to fix the issue.
To avoid issues with a DMARC ESP, it's important to select a reliable and trustworthy ESP that has a proven track record of providing effective DMARC authentication and protection services. Additionally, it's important to regularly monitor email activity and reporting to quickly identify and address any issues or inconsistencies that may arise.
Monitor Email Activity
Monitor your email activity and DMARC reports regularly to ensure that DMARC authentication is working as intended. This will help you identify and address any issues or inconsistencies quickly.
Fixing DMARC failures requires a careful review of your email authentication settings and DNS records, along with adjustments to your DMARC policy if necessary. By following these steps and working with your email service provider as needed, you can improve email security and protect against email fraud and phishing attacks.
Final Thoughts
DMARC provides a powerful tool for improving email security and protecting against email fraud and phishing attacks. By implementing DMARC, individuals and organizations can enjoy increased email deliverability, improved visibility into email activity, and enhanced brand reputation, while also ensuring compliance with email security standards. Along with the implementation, every business should also be prepared when this tool suddenly fails so that you can prevent or avoid losses in your business.

Leave a comment!