Malware, short for malicious software, is a type of software intentionally designed to cause harm to computer systems, networks, and devices, or to steal sensitive data from users without their knowledge or consent. Malware can take many forms, including viruses, trojan horses, worms, spyware, adware, ransomware, and more.
Malware can be spread through various means, such as phishing emails, infected software downloads, malicious websites, and compromised networks.
These types of malware are constantly evolving as new ones are developed and existing ones are modified or repackaged. Additionally, many malware variants are created with the purpose of evading detection and may go undetected for a significant period of time. One of the latest malware detected is the Qbot Malware, wherein it attacks email by using PDF and WSF combo to install malware.
What is Qbot Malware and How It Started
Qbot, also known as QakBot or Pinkslipbot, is a sophisticated banking Trojan that first emerged in 2009. Qbot is primarily designed to steal sensitive financial information, such as online banking credentials, credit card details, and other personal data. It is primarily distributed through email spam campaigns and exploit kits.
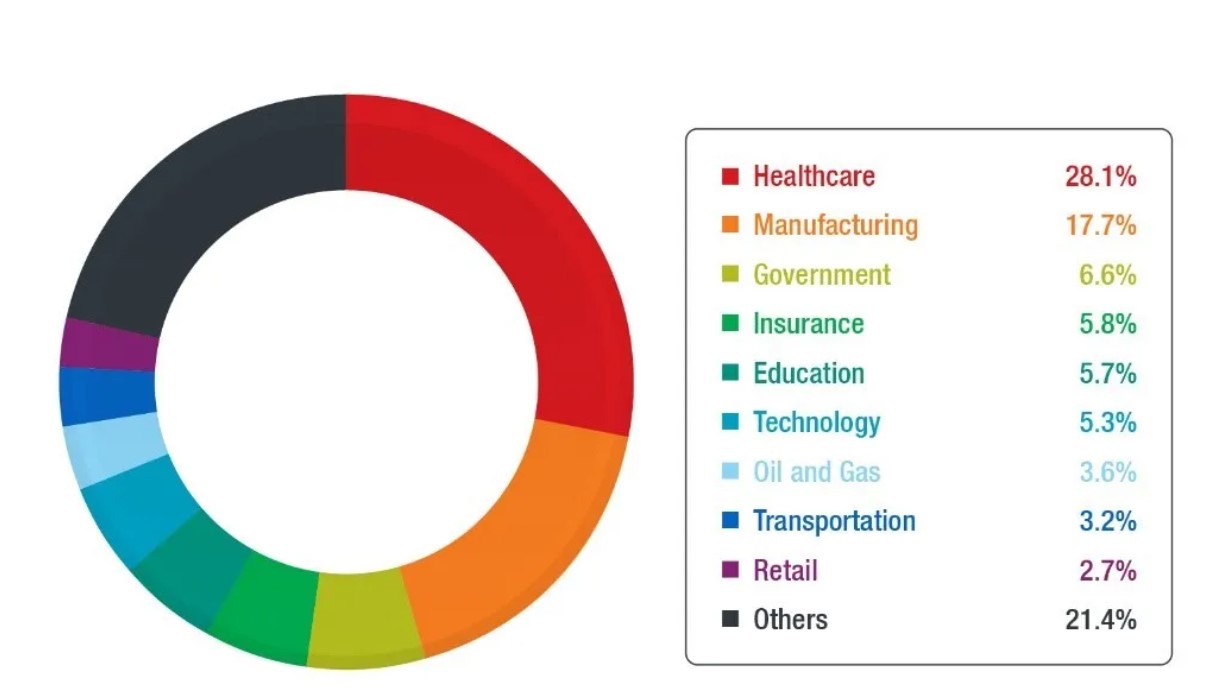
According to a report from Trend Micro, in 2020, there were a total of 3,893 unique Qakbot detections. A spike in this detection was discovered in January with over 1,400, which slowed down in February and March. It went back up in April with over 1,000. Among the detected malware from each industry, healthcare was the most affected with 256 unique detections from the same period, followed by manufacturing and government with 161 and 60, respectively.
Source: Trend Micro, Qakbot Resurges, Spreads through VBS Files
The initial infection vector of Qbot is typically through malicious email attachments or malicious links within emails. These emails are carefully crafted to appear legitimate and often use social engineering techniques to trick users into opening the attachments or clicking on the links. Once a user interacts with the malicious payload, Qbot is downloaded and executed on the victim's system.
What are Qbot's Capabilities and Impact
Over the years, Qbot has evolved and added new features and capabilities. It has incorporated advanced techniques to evade detection, such as anti-analysis mechanisms, rootkit functionality, and encryption to protect its command and control communication.
Qbot has the ability to propagate within a network by exploiting vulnerable systems and by using stolen administrative credentials. It can spread laterally and infect other devices connected to the same network. Qbot also has the capability to create a botnet, allowing attackers to control and coordinate infected devices for various malicious activities.
Qbot has been responsible for a significant number of financial fraud cases, including large-scale banking thefts and wire fraud. It continues to be actively developed and maintained by cybercriminal groups who profit from its capabilities. While this type of malware continues to develop, it may have a significant impact on businesses. Here are some of the potential impacts:
Financial Loss
Qbot is primarily designed to steal financial information, including online banking credentials and credit card details. Businesses that fall victim to Qbot may suffer financial losses due to unauthorized transactions, fraudulent wire transfers, or compromised customer payment information.
Data Breach
A data breach refers to an incident where unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive or confidential data, potentially compromising its confidentiality, integrity, or availability. It involves the unauthorized acquisition, disclosure, or access of sensitive information by cybercriminals or malicious actors.
Qbot's ability to exfiltrate sensitive data means that businesses could experience data breaches. This can lead to the exposure of confidential business information, trade secrets, customer records, and other valuable data, resulting in reputational damage and potential legal and regulatory consequences.
Disruption of Operations
If Qbot infects critical systems within a business network, it can disrupt operations by causing system crashes, data corruption, or unauthorized access. This can result in downtime, loss of productivity, and disruption to customer services.
Compromised Customer Trust
If customer data, including personally identifiable information (PII), is compromised due to Qbot infections, it can erode customer trust. Businesses may face reputational damage and a loss of customer confidence, impacting customer relationships and future business opportunities.
Compliance and Legal Issues
Businesses operating in regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, or data-sensitive sectors, may face compliance and legal issues if Qbot compromises systems containing sensitive information. This can result in fines, penalties, and potential legal actions for non-compliance with data protection and privacy regulations.
Additional Malware and Attacks
Qbot's ability to create botnets and distribute spam emails increases the risk of additional malware infections. This can open the door for further attacks, such as ransomware, data breaches, or distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, exacerbating the impact on businesses.
How Qbot Malware Works
Qbot employs a variety of attack vectors to infect its victims. One of the primary methods is phishing emails that contain malicious documents, attachments, or password-protected archives with the documents enclosed. These phishing emails are designed to deceive recipients into opening the attachments or accessing the enclosed documents, thereby initiating the infection process. Here is a general overview of how Qbot works:
Initial Infection
Qbot typically enters a system through phishing emails or malicious attachments. The emails are carefully crafted to appear legitimate and often use social engineering techniques to trick users into opening the attachments or clicking on malicious links.
Dropper Execution
Once the user interacts with the malicious payload, Qbot's dropper component is executed. The dropper is responsible for downloading and installing the main Qbot malware onto the infected system.
Persistence and Concealment
Qbot employs various techniques to ensure persistence and avoid detection. It may create registry entries or modify system files to automatically execute each time the system starts. Qbot can also hide its presence by using rootkit techniques to manipulate the operating system's behavior and evade detection by security software.
Command and Control Communication
Qbot establishes communication with its command and control (C&C) servers. This communication allows the malware operators to remotely control and command the infected systems. Qbot uses various protocols and encryption methods to protect this communication and ensure that it remains hidden from security monitoring.
Data Theft and Credential Harvesting
Qbot's primary objective is to steal sensitive information, particularly financial credentials. It can capture keystrokes, log user activity, and inject malicious code into web browsers to gather additional information during online banking sessions. Qbot focuses on capturing online banking credentials, credit card information, and other financial data.
Network Propagation and Lateral Movement
Qbot has the ability to propagate within a network, infecting other devices and systems. It can exploit vulnerabilities in network services or use stolen administrative credentials to move laterally within the network, searching for additional targets to infect.
Botnet Creation and Malicious Activities
Qbot can recruit infected systems into a botnet, allowing the malware operators to control a network of compromised devices. This botnet can be utilized for various malicious activities, such as distributing spam emails, launching further attacks, or coordinating large-scale campaigns.
Qbot Malware Features and Capabilities
Qbot malware possesses a range of capabilities that make it a potent threat. Here are some of its key capabilities:
Information Theft
Qbot specializes in stealing sensitive information, particularly financial credentials. It can capture login credentials for online banking accounts, credit card information, and other financial data from infected systems.
Keylogging and Credential Theft
Qbot includes keylogging functionality, which allows it to record keystrokes and capture sensitive information entered by users, such as usernames, passwords, and other authentication details.
Web Injects
Qbot has the ability to inject malicious code into web browsers, enabling it to manipulate web pages and gather additional information during online banking sessions. This technique often tricks users into providing more data, such as security questions or one-time passwords.
Network Propagation
Qbot can propagate within a network, infecting other devices and systems. It achieves this by exploiting vulnerabilities in network services or by using stolen administrative credentials to move laterally within the network.
Botnet Creation
Qbot can create a botnet, a network of compromised computers under the control of the malware operators. This allows the attackers to remotely control the infected systems, distribute commands, and coordinate large-scale attacks.
Spam Email Distribution
Qbot can send out spam emails from infected systems to further spread itself and distribute additional malware or phishing campaigns.
Anti-detection Techniques
Qbot employs various anti-detection mechanisms to evade security software and analysis. It can use rootkit functionality to hide its presence, employ encryption to protect communication with command and control servers, and use polymorphic techniques to generate unique variants that are more difficult to detect.
It's important to note that Qbot is a highly adaptable malware, and its capabilities may evolve and change over time as new versions and variants are developed by its operators.
How To Prevent Qbot Attacks
Qbot remains a persistent and dangerous malware, with its threat group continually evolving its techniques over time. Given that Qbot is commonly distributed through phishing emails, one of the most effective methods to safeguard against this malware is by implementing Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) for email.
ATP for email is a comprehensive security solution designed to detect and block malicious emails, including those carrying Qbot payloads. By leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning, and real-time threat intelligence, ATP can identify and neutralize phishing attempts, malicious attachments, and suspicious links associated with Qbot and other malware strains.
There are also other cybersecurity measures that businesses might consider to prevent Qbot attacks:
Employee Education and Awareness
Train your employees on cybersecurity best practices, including how to identify phishing emails, suspicious attachments, and malicious links. Encourage them to exercise caution when opening emails or downloading files from unknown sources.
Email Filtering and Spam Detection
Implement robust email filtering and spam detection systems to reduce the likelihood of phishing emails containing Qbot payloads reaching employees' inboxes. This can help block malicious attachments or links associated with Qbot and other malware.
Strong Password Policies
Enforce strong password policies across your organization. Encourage employees to use unique, complex passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. This can make it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
Regular Software Updates and Patching
Keep all software, including operating systems, applications, and security solutions, up to date with the latest patches and updates. This helps address known vulnerabilities that malware like Qbot can exploit.
Robust Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions
Deploy reliable antivirus and anti-malware solutions across your organization's systems. Regularly update and scan systems to detect and remove any potential malware infections, including Qbot.
Network Segmentation
Implement network segmentation to compartmentalize your network and restrict unauthorized lateral movement. This can limit the spread of malware within your network and help contain potential Qbot infections.
Secure Remote Access
If remote access is required for your business operations, ensure that secure remote access protocols, such as VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) with strong encryption and proper authentication, are in place. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential Qbot infections.
Regular Data Backups
Maintain regular backups of your critical data and verify their integrity. In the event of a Qbot infection or any other cybersecurity incident, having up-to-date backups can help you restore your systems and data without paying a ransom or suffering from permanent data loss.
Incident Response Planning
Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a Qbot infection or any other security incident. This ensures a prompt and effective response to mitigate the impact and minimize potential damage.
Security Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Implement robust security monitoring tools and systems that can detect and alert you to potential Qbot infections or suspicious activities. Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity threats and subscribe to threat intelligence services to proactively identify and respond to emerging Qbot-related threats.
If businesses aren’t sure how to handle this kind of attack, there are also other options such as getting a professional managed service provider. These MSPs can help in your overall IT structure, and network monitoring as well as the ability to detect and neutralize cyberattacks using robust tools.
Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing effort. Regularly assess and update your security measures, stay informed about emerging threats, and foster a culture of security within your organization to effectively protect against Qbot attacks and other evolving malware threats.

Leave a comment!